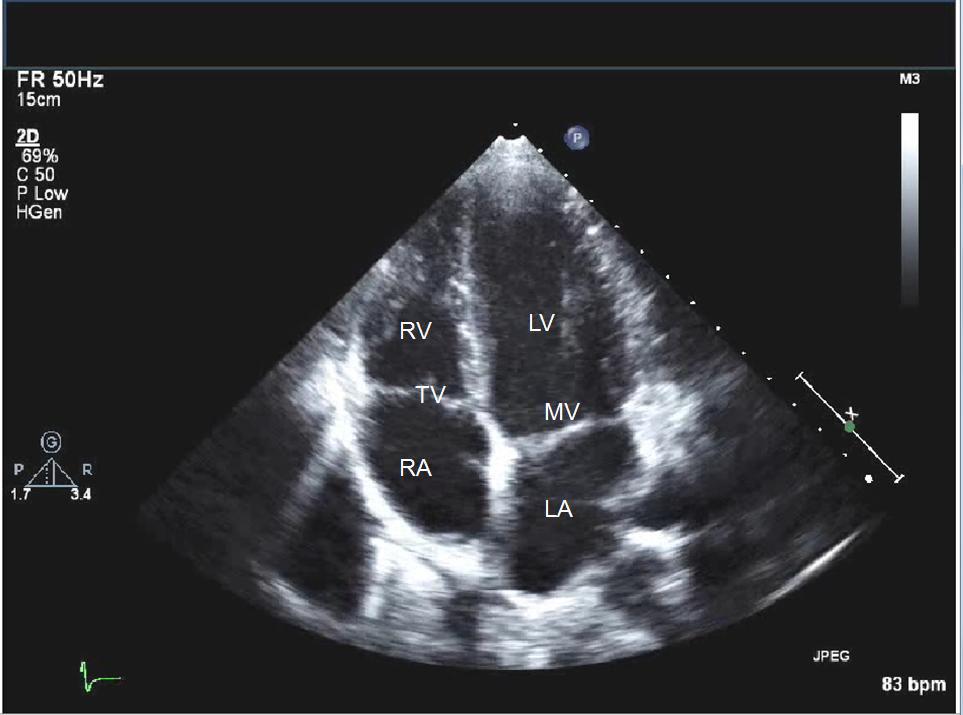
Echocardiogram (echo)
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart using high frequency sound waves to evaluate the structure of the heart, its chambers, walls and valves, the surrounding major blood vessels and the pericardial sac. These sound waves are generated from a probe called a transducer. The sound waves are bounced off the internal structures to produce images and video. No x-rays are involved in this technique. The test usually takes about 20 minutes to perform.
The test can be done with the transducer placed on the chest wall to produce the ultrasonic image. This is the most common form of echo and is called a Transthoracic Echocardiogram or TTE.
The test can also be done with the transducer gently guided down the throat into the esophagus. From there sound waves are emitted through the esophagus and directed at the heart to obtain the ultrasonic images. This is a more invasive test and is only done in very specific circumstances. The throat is numbed and medication is used to relax the patient. This is called a Transesophageal Echocardiogram or TEE.
Doppler ultrasound is used to help determine the speed and direction of the blood flow in your heart. The Doppler techniques are used in most TTE’s and TEE’s. Sometimes the Doppler flow is shown in color.
Video is taken throughout the procedure and then a cardiologist interprets the results.
Dr. Moore only performs the Transthoracic Echocardiogram. (TTE)
What will this test show?
- The size and shape of the heart
- The thickness and movement of the heart walls
- The Ejection Fraction (the heart’s pumping strength)
- The function of the heart valves including leakage (regurgitation), damage that can occur from infection or tumors and narrowing (stenosis) of the valves
- Congenital abnormalities (condition present from birth)
- Blood clots in the chambers of the heart
- Abnormalities of the outer lining of the heart, the pericardium, such as a collection of fluid (pericardial effusion)
- Abnormalities of the large blood vessels that enter and leave the heart
When is an echo needed?
- An abnormal bedside physical exam
- Symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain
- Suspected heart failure, cardiomyopathy or congenital abnormality
- The use of certain cardio-toxic medications
- Suspicion of infection of a heart valve or fluid around the heart
What to expect with your test?
You will lie on a table and a technician will place electrodes on your chest. During your test an EKG keeps track of your heartbeat. The room will be dark and gel will be placed on your chest. The transducer will be placed on your chest and moved to different positions to get different views of your heart and the surrounding structures. A cardiologist will review the video and pictures.
What are the risks of the Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
There are no risks involved with this test.
How to prepare for the Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
There are no special instructions. You can eat or drink as you usually would. Avoid using lotions on the chest.
What to expect after your test
The gel will be wiped off your chest and you will be allowed to sit up. The electrodes will be removed.
You will receive a preliminary report of your test immediately. Then a cardiologist will read your test and if there is anything different from the preliminary report, you will be contacted. This usually takes one week.
